About Mud
MUD is an open-source engine for building autonomous worlds and fully onchain applications on Ethereum. Developed by Lattice, MUD simplifies the process of building modular, scalable, and performant EVM apps by offering a tightly integrated software stack. It abstracts away complex backend and synchronization issues, enabling developers to focus on application logic and world-building.
Designed for developers pushing the limits of onchain design, MUD has powered dozens of high-performance applications such as OPCraft and EVE Frontier. With its unique approach to storage, access control, and synchronization, it enables the creation of onchain games, multi-user worlds, and programmable dApps that go far beyond the capabilities of traditional smart contract platforms.
MUD began as a response to real-world challenges faced while building onchain games like Dark Forest and zkDungeon. These early projects highlighted how difficult it was to manage onchain state, maintain upgradability, and synchronize game logic between blockchain and frontend. This inspired the creation of a new kind of engine — one that would not only manage storage efficiently but also unify the entire development stack from contract to client.
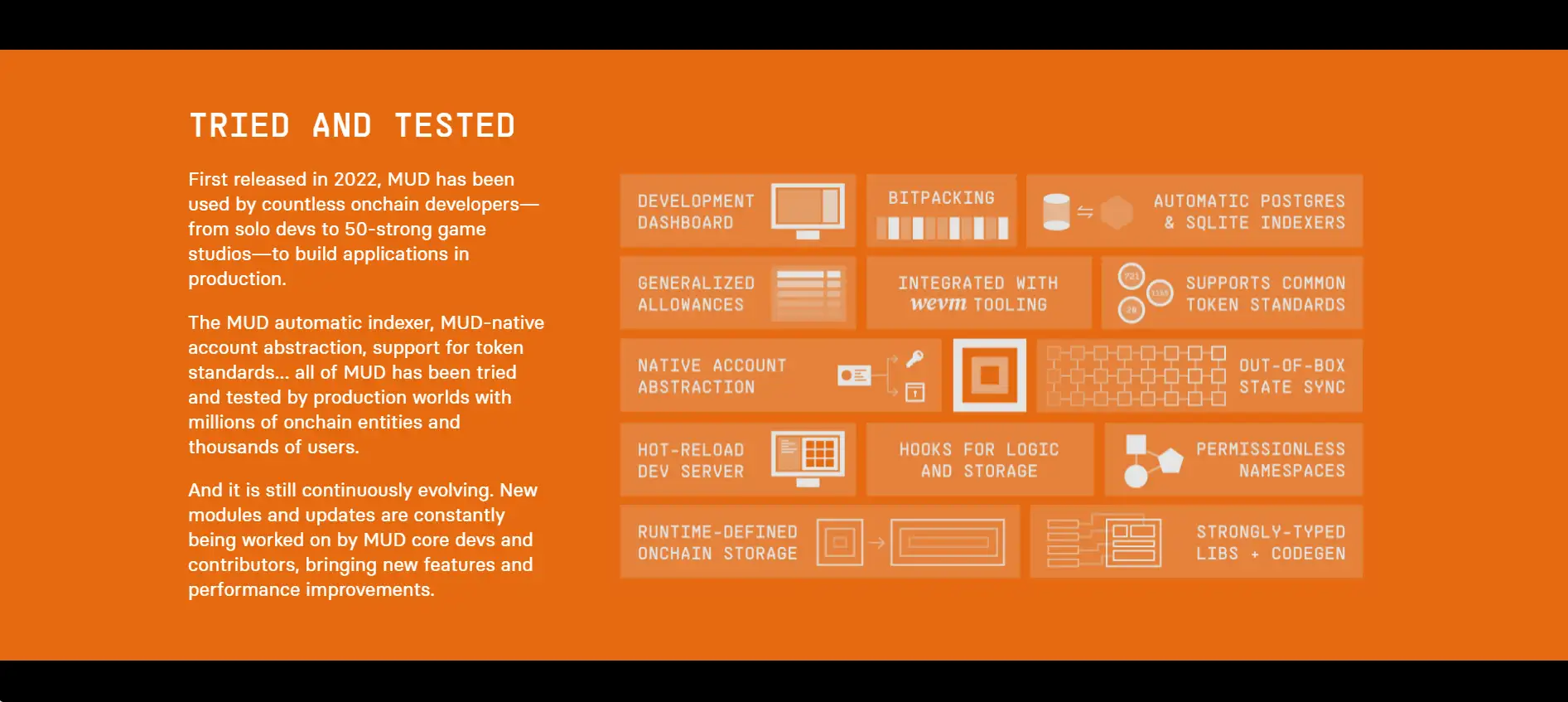
Unlike traditional EVM development, which often requires separate efforts to build contracts, write indexers, and sync frontend apps, MUD offers a holistic development framework. It provides a familiar relational data model via its custom Store engine, allowing developers to define data schemas and interact with them like they would with a database. Events are automatically emitted and indexed, enabling real-time state reflection without additional infrastructure.
The World component acts as the access-controlled logic layer above Store. It enables permissioned or permissionless System contracts to extend a shared onchain world, similar to plug-ins or facets in the Diamond standard — but with built-in support for namespaces and third-party extensions. Systems can interact across namespaces, creating truly modular applications while still retaining fine-grained access control.
MUD has been adopted by both independent developers and full-scale studios. Projects like Biomes, Words3, Dappmon, and PopCraft were built using MUD’s architecture. The framework's modularity and efficiency have also made it ideal for complex simulations, high-frequency games, and onchain infrastructure tools.
With over 30+ live projects and a fast-evolving open-source ecosystem, MUD is setting the standard for what it means to build maximally onchain apps. It competes with tools like Foundry, Hardhat, and Ethers.js, but goes much further by unifying the entire lifecycle of development, deployment, and user interaction into one composable system.
MUD provides a set of advanced features that redefines what’s possible when building Ethereum applications:
- Integrated Software Stack: Combines storage, logic, indexing, and frontend syncing in one framework with no glue code required.
- Relational Data Model on Ethereum: The Store engine models data as typed tables and records, supporting familiar developer workflows.
- Automatic Indexing: Events are emitted on every change, allowing clients to stay in sync with onchain state in real time without writing custom indexers.
- World-Based Access Control: A centralized logic entry point ensures secure execution while enabling extensibility through permissionless namespaces.
- Maximally Onchain Applications: The full application state resides on the EVM — no separate backends or middleware required.
- Built-in Developer Tools: Features like hot reloading, modular templates, and support for ERC-4337 bundlers reduce development friction.
- Production Ready: Used by games and applications handling millions of transactions, such as OPCraft’s 3.5M+ interactions in 10 days.
- Open Source and Extensible: Fully open under the MIT license, with a thriving contributor base and actively maintained core modules.
MUD is easy to get started with, thanks to its flexible templates and comprehensive documentation:
- Step 1 – Install Dependencies: Ensure you have Node.js v20, pnpm v8+, Git, and optionally Foundry installed.
-
Step 2 – Create a New Project: Run
pnpm create mud@latestto scaffold a new MUD project using one of the available templates like Vanilla, React, or Three.js. - Step 3 – Choose Your Template: During setup, select from multiple frontend options like React-ECS, Phaser, or Three.js to customize how your world will be visualized.
-
Step 4 – Start Development Server: Use
pnpm devto spin up the dev environment with automatic contract hot-reloading and synchronized client updates. - Step 5 – Explore the Architecture: Your project will include two main packages: contracts (onchain logic) and client (offchain UI). Make changes in either to extend your world.
- Step 6 – Deploy on EVM Chains: Use Quarry or your preferred ERC-4337 compatible bundler to deploy your world with ultra-low latency.
Mud FAQ
MUD includes a built-in automatic indexer that emits structured events on every table mutation. This enables offchain systems to mirror the onchain state into a relational database without writing custom event handlers or synchronization logic. Your frontend stays synced automatically, significantly reducing development time. Learn more at MUD.
Yes, MUD’s permissionless namespace system allows anyone to claim an unused namespace and deploy custom tables and systems. This means developers can independently extend existing worlds, create plugins, or build companion apps — without altering the original codebase. It supports a new level of onchain composability.
MUD centralizes logic execution through the World contract, which authorizes or denies actions based on namespace-level access control. All calls are routed through this secure gatekeeper, and permissioned System contracts execute logic accordingly. This modular security design enables collaborative development without compromising control. Visit MUD for full architecture details.
MUD stores the entire application state directly in the EVM, eliminating any need for external servers, custom backends, or offchain logic. Clients interact directly with the chain and can use the standardized data model to retrieve state. This ensures total transparency, auditability, and decentralization, unlike hybrid solutions. Explore the stack at MUD.
MUD is engineered for scale, featuring a custom storage engine that packs data tightly and indexes it automatically. In real-world examples like OPCraft, MUD supported 3.5 million transactions in just 10 days. Its performance, low-latency sync, and gas-optimized writes make it ideal for high-performance onchain games.
You Might Also Like