About Beanstalk
Beanstalk is a fully decentralized, algorithmic stablecoin protocol built on Arbitrum that enables a permissionless, rent-free economy. The core idea behind Beanstalk is to create a stablecoin, Bean, that does not rely on collateral or centralized control to maintain its value. Instead, it operates using a system of incentives, debt issuance, and supply adjustments designed to keep the price of 1 Bean as close as possible to $1 in a sustainable manner.
By utilizing a credit-based model, Beanstalk offers a new approach to decentralized finance (DeFi) that removes capital inefficiency associated with overcollateralization. Its mechanisms are designed to promote long-term price stability, encourage ecosystem growth, and offer yield opportunities through protocol-native systems like the Silo and Field. Beanstalk aims to serve as the foundational layer of a new generation of DeFi applications and services.
Beanstalk is a comprehensive protocol redefining the mechanics of stablecoin issuance by eliminating the need for collateral and focusing on algorithmic, incentive-driven price stabilization. It functions on a credit-based seigniorage model that allows the supply of Bean to contract or expand based on market demand. This dynamic adjustment mechanism forms the heart of the protocol’s peg maintenance strategy, where price fluctuations around $1 are corrected by either issuing new tokens or incentivizing debt purchases via “Soil”.
The system is structured around multiple interconnected components, including the Silo, which provides yield to depositors via Bean seigniorage; the Field, where users lend Beans in return for “Pods” (the protocol’s debt asset); and the Barn, which was implemented post-exploit in April 2022 to facilitate recapitalization through “Fertilizer”. The entire protocol operates as an EIP-2535 Diamond Standard contract, allowing modular, gas-efficient upgrades and expansion through facets.
On a technical level, Beanstalk leverages Solidity v0.8.20 and employs the AppStorage pattern to enable shared state across facets, optimizing gas usage. Each facet handles specific logic such as Deposits, Conversions, Permissions, and Pod Market trading. The internal design allows users to perform composable actions (farming) in a single transaction using “Internal Balances”.
Beanstalk’s broader vision is to create an interoperable, composable financial layer native to Arbitrum and open to integration by external protocols. It removes barriers seen in centralized stablecoins and collateralized models, opening the door to more dynamic and inclusive economic systems. In doing so, it competes conceptually with other algorithmic and non-collateralized stablecoin protocols like Ampleforth, Fei Protocol, and Frax—while offering its own innovations in credit mechanics and DAO-controlled governance.
Beanstalk offers a number of innovative features and benefits that distinguish it in the decentralized stablecoin and DeFi infrastructure landscape:
- Collateral-Free Stability: Unlike most stablecoins, Bean is not backed by overcollateralized or custodial assets. Instead, it uses an algorithmic credit-based model to maintain its peg, offering an entirely decentralized monetary system.
- Modular Smart Contract Architecture: Built using the EIP-2535 Diamond Standard, Beanstalk allows flexible and efficient upgrades through its Facet system while minimizing gas costs and contract bloat.
- Autonomous Peg Maintenance: The protocol autonomously responds to market conditions by either minting new Beans when the price is high or offering credit via Soil when the price is low. This creates a self-regulating, market-driven stabilization mechanism.
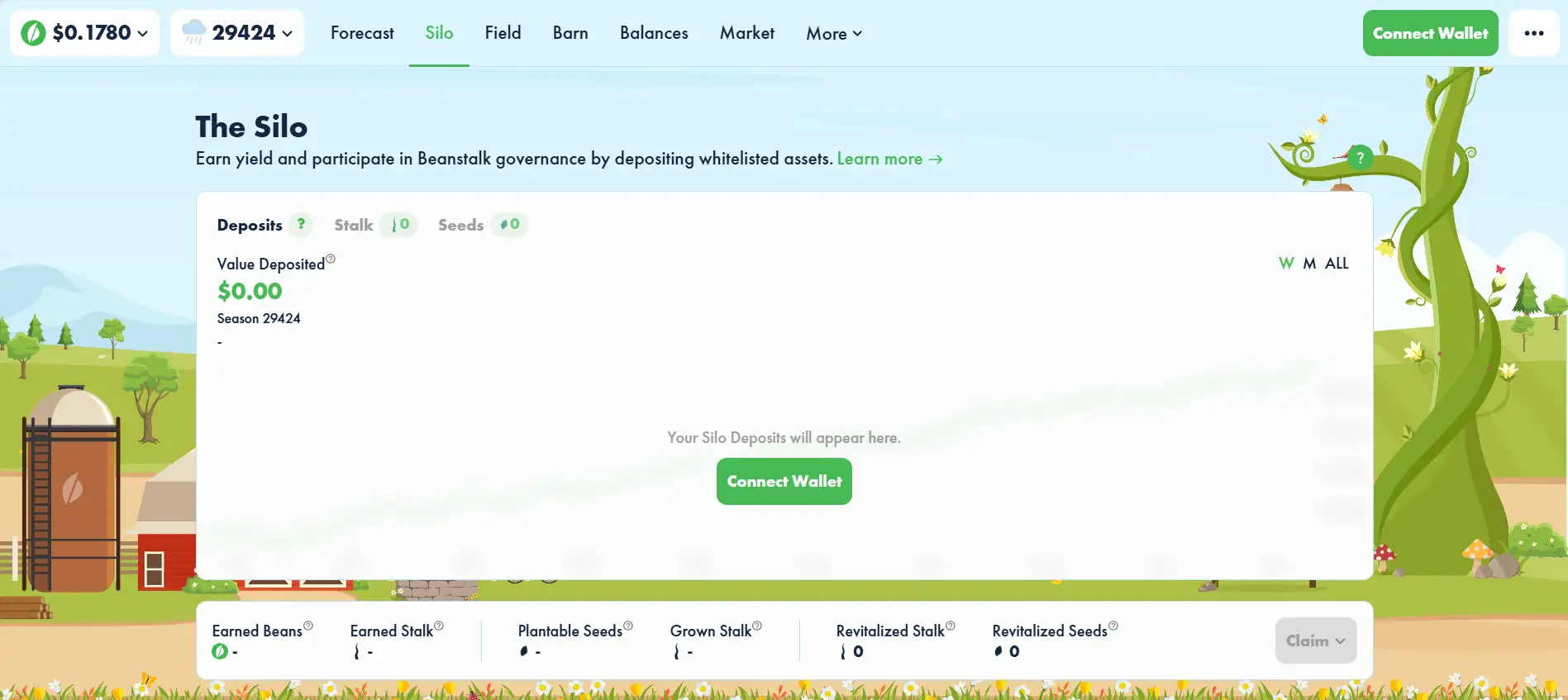
- Passive Yield Through the Silo: Users can deposit assets into the Silo to earn yield in the form of Stalk and Seeds, incentivizing long-term participation and providing utility to the stablecoin.
- Decentralized Debt Market: The Field acts as a credit facility where users lend to the protocol in exchange for Pods, which are repaid on a FIFO basis—introducing a trustless, decentralized credit system to DeFi.
- Zero-Fee On-Chain AMM: The Pod Market and integrations with liquidity pools support fee-free trading of certain assets, increasing capital efficiency and lowering barriers for arbitrage.
- Community Governance: The protocol is governed by the DAO, giving the community control over upgrades, parameters, and protocol direction.
Beanstalk makes it easy for users to begin participating in its decentralized economy through a set of intuitive interfaces and integrations:
- Create a Wallet: If you don’t already have a Web3 wallet, start by setting one up (e.g., MetaMask). Ensure it's connected to the Arbitrum network.
- Visit the Official Site: Navigate to bean.money and access the Beanstalk UI.
- Explore the Silo: Deposit Beans or other whitelisted assets into the Silo to start earning yield via Stalk and Seeds. These represent your share of protocol rewards and governance rights.
- Utilize the Field: Lend Beans to the protocol by sowing Soil and receive Pods in return. Pods are repaid in a FIFO manner and are tradable on the Pod Market.
- Monitor Peg Movements: Watch how Bean maintains its dollar peg and take part in peg maintenance mechanisms like Convert and Swap.
- Use Beanstalk Docs: For detailed instructions and smart contract references, check out the Farmers’ Almanac, which provides all official documentation and usage guides.
Beanstalk FAQ
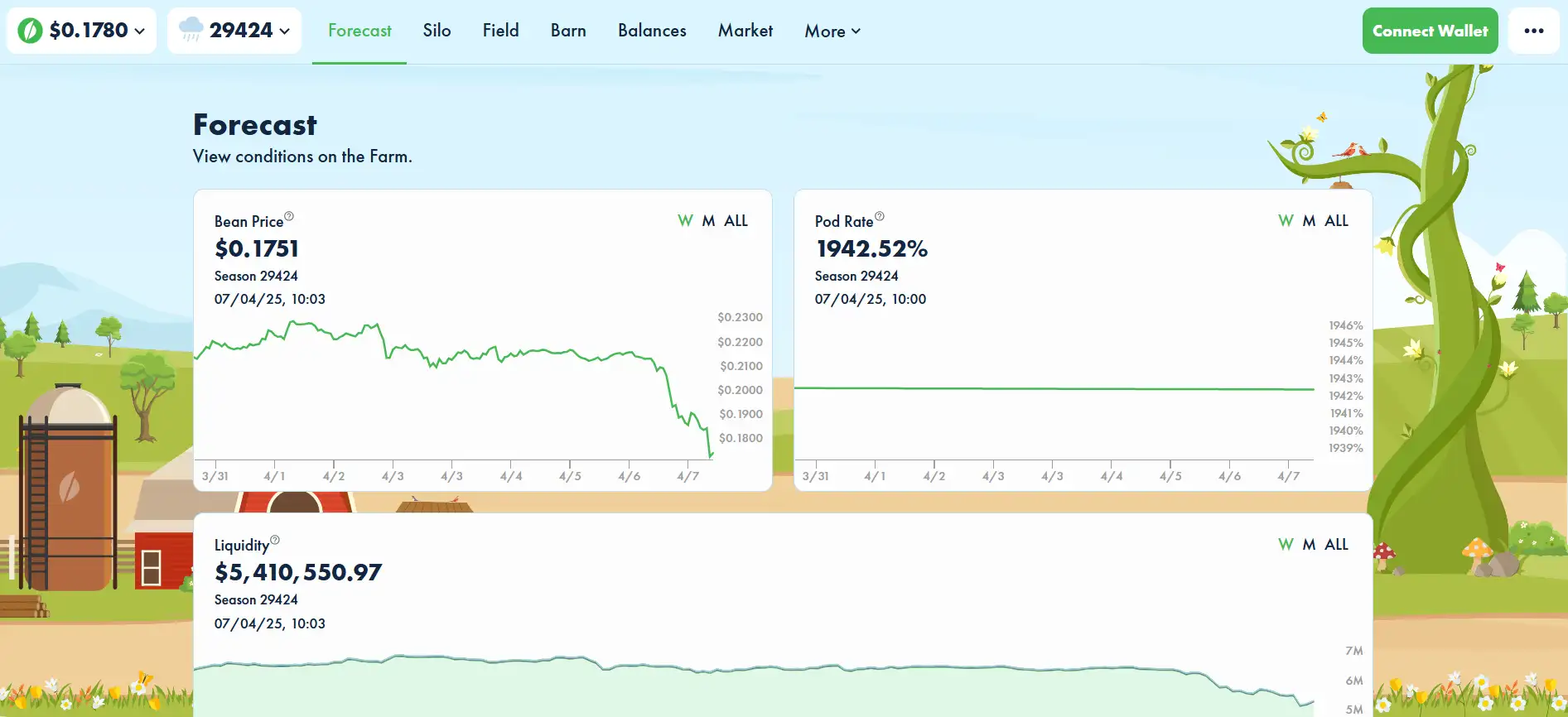
Soil in Beanstalk represents available lending capacity. When Bean trades below $1, the protocol issues Soil as a signal to borrow Beans from the market. Users who Sow Beans into this Soil receive Pods, Beanstalk’s debt tokens, which are repaid in a First-In-First-Out (FIFO) manner. This creates an autonomous credit issuance mechanism that helps reduce Bean supply and restore the price peg without collateral. More details are available on bean.money.
Beanstalk relies on market incentives and algorithmic adjustments instead of collateral. When the price of Bean exceeds $1, the protocol mints new Beans; when it drops below, it offers Soil to borrow and burn Beans. These mechanics adjust supply in real-time, encouraging arbitrage opportunities that bring the price back to its $1 target. The entire model is non-custodial and governed by its DAO via bean.money.
Farmers are active participants in the Beanstalk ecosystem, engaging in Sowing, Harvesting, and Depositing. This metaphor is woven into the protocol's mechanics, where yield-bearing activities mirror farming cycles. Depositing into the Silo grows Stalk and Seeds, while lending to the protocol returns Pods. The farming theme reflects long-term, cyclical engagement and reinforces how users support peg stability. Learn more at bean.money.
Beanstalk is implemented using the EIP-2535 Diamond Standard, which allows it to split its logic into modular components called Facets. Each Facet can be independently upgraded or replaced, offering flexibility, gas savings, and scalability. This architecture avoids the limitations of monolithic smart contracts and ensures Beanstalk can evolve without redeployment. It supports complex features like composability and peg management across contracts. Technical details are available at bean.money.
Pods are Beanstalk’s debt instruments received when users Sow Beans during a supply contraction. They’re repaid in a FIFO queue once conditions allow new Bean minting. The Pod Market is a secondary exchange where Pods can be bought and sold before maturity, offering liquidity and price discovery. This system enables a decentralized and transparent credit layer within Beanstalk, and it’s accessible directly through the interface at bean.money.
Seasons are Beanstalk’s native unit of time, representing roughly one hour intervals. Each new Season begins with a successful execution of the
gmfunction, which triggers key protocol operations. This system ensures decentralized timekeeping and protocol execution without reliance on off-chain schedulers. To incentivize participation, the user who successfully callsgmreceives freshly minted Beans as a reward. This structure promotes efficient and timely updates while reinforcing the permissionless ethos of Beanstalk.The Depot acts as Beanstalk’s gateway for seamless, gas-efficient interactions with other Ethereum-native protocols. It enables users to execute complex DeFi operations in a single transaction by integrating external Pipelines. These Pipelines can be added or modified via governance. This setup significantly reduces friction for users and maximizes the utility of Beanstalk within the broader Ethereum DeFi ecosystem, reinforcing its goal of low-cost and high-composability finance.
Beanstalk is engineered to reduce concentration of power through its unique incentive mechanisms. The Stalk System rewards long-term Deposits while simultaneously diluting older positions over time via the Grown Stalk mechanics. This system creates a natural decentralization of governance influence by distributing more rewards to newer Depositors. Additionally, there's no pre-mine or privileged allocation—Beans are only minted through user participation, ensuring a fair and inclusive environment.
Beanstalk is engineered with efficiency at its core by leveraging both the Pipeline and Depot contracts. These systems allow users to execute complex, multi-step transactions—such as harvesting, converting, and withdrawing—with minimal gas overhead. By batching multiple operations into a single call, users can significantly reduce transaction costs while maintaining high on-chain composability. This design ensures that gas efficiency does not come at the expense of decentralization or user autonomy.
Reward distribution in Beanstalk is governed by the Stalk and Seed system, which determines how newly minted Beans are allocated. Depositors receive Stalk for governance power and yield, and Seeds that grow into more Stalk over time. However, to avoid long-term monopolization, the protocol implements dilution mechanisms—older deposits earn proportionally less new Stalk, balancing the influence of early and new participants. This model encourages continued participation while preserving equity across users.
You Might Also Like